Although every state has slight differences in laws regarding sexual offenders, all convicted sex offenders are expected to comply with registration requirements no matter where they decide to live or work. Here’s what you need to know about sex offender registration in Nevada.
As per Nevada’s NRS 179D.4411, every offender convicted of a crime against a child and every sex offender must initially register with the local law enforcement agency of the jurisdiction in which the offender or sex offender was convicted. Following that, they must also register within the jurisdiction they live/reside, go to school, or work.

What information is required to register as a sex offender? When registering with the local law enforcement agency, NRS 179D.4432 states that the offender should be prepared to provide the following.
If the offender or sex offender hasn’t already provided a biological specimen, he/she will provide a biological specimen to the local law enforcement agency where he/she is registering as an offender. The agency will then provide the sample to a forensic lab designated by the county.

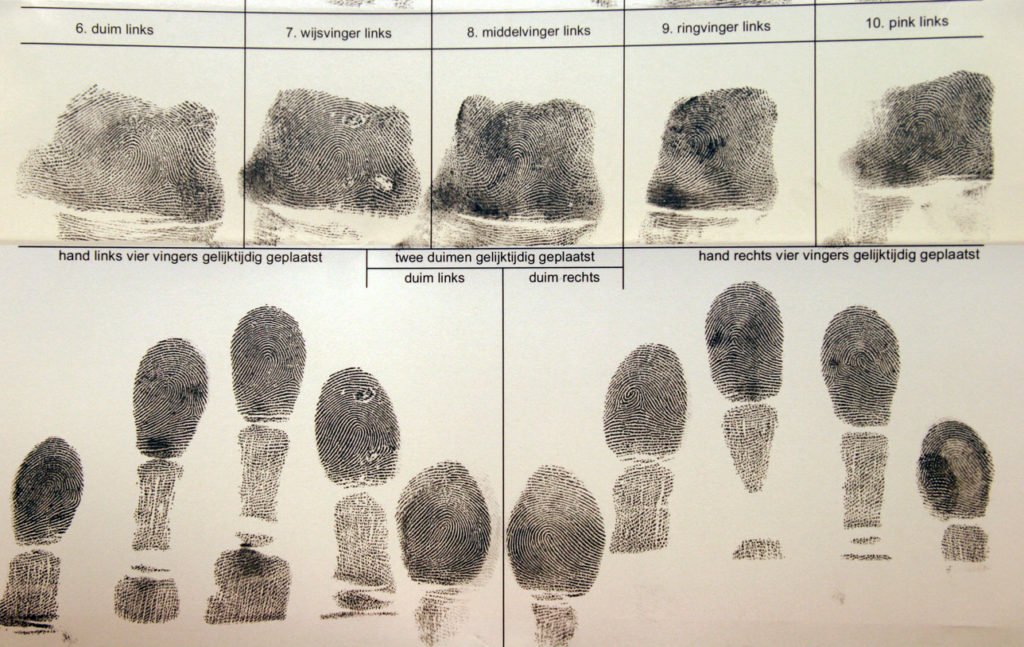
The local law enforcement agency will also ensure they have gathered a complete physical description of the sex offender, a current picture, fingerprints, and palm prints. Other information that may be collected includes:
It is the offender’s duty to inform the local law enforcement agency of any change of name, residence, employment, student status, or other vital differences, as per NRS 179D.4473. The change(s) must be reported no more than three business days after they have been made.
How long can a sex offender live in a neighborhood before they have to register? NRS 179D.4604 states that registration with a local law enforcement agency must be made within 48 hours of the offender living there. That means, even if the offender committed the offense(s) in a different neighborhood, city, or state and already registered with the local law enforcement agency in that state (as they are legally obligated to do), they still must register with the local law enforcement agency where they currently reside within 48 hours of being present there.
This rule applies even if they live with a family member, a friend, a partner, or in a short-term rental. As long as they are residing there for 48 hours, they must register with the local law enforcement agency.
If the offender is a nonresident of the state but is a worker or student within the state, they must still register at the appropriate sheriff’s office, metro police department, or city police department where they work or are a student, no more than 48 hours after having started working or becoming a student there. It will then be the local law enforcement agency’s responsibility to forward the offender’s information to the Central Repository, including the fingerprints and photograph.
What happens if the sex offender fails to register or falsifies the necessary information to the local law enforcement agency? If a sex offender fails to register with a local law enforcement agency, or fails to notify the agency of a change in name, residence, or employment or student status, or provides false or misleading information to the Central Repository or local law enforcement agency, that individual is now guilty of a Category D Felony and shall be punished as provided in NRS 193.1305.
A Category D Felony is a felony for which a court shall sentence the convicted person to imprisonment in the State Prison for a minimum term of 1 year and maximum term of 4 years. In addition, the court may also fine up to $5,000 – unless a greater fine is authorized or required by statute.
The Central Repository will keep all information updated. From there, information is dispensed to the Attorney General, the appropriate law enforcement agencies for each jurisdiction in which the offender resides or is a student or worker, all agencies responsible for conducting employment-related background checks, and any organization, company, or person who requests such notification.
The local law enforcement agency will provide all updated information from the Central Repository to each school, religious organization, youth organization, and public housing authority in which the offender or sex offender resides or is a student or worker. The information will also go to each agency that provides child welfare services and volunteer organizations in which contact with children may occur. Again, this information may also be requested by any organization, company, or person who requests it.

Convicted sex offenders in Nevada are required to go to the DMV in person to conduct all driver’s license-related services. They may not use the kiosks, mail in their information, or complete business over the internet.
If a sex offender fails to register as a sex offender in Nevada, their driver’s license renewal will be denied after their current license expires. Relevant to note: convicted sex offenders are required to renew their licenses every year in Nevada.
Can non-citizen sex offenders be deported? The short answer is “yes.” But it depends. Remember: non-legal (i.e., illegal) aliens can be deported from the U.S. at any time, regardless of whether or not they are convicted of a sex crime.
Legal non-citizens living in the U.S. may also be deported from the U.S. if the nature of their crime was an aggravated felony, a firearms offense, a drug crime, a domestic violence offense, or a crime involving moral turpitude. Sex-related crimes involving moral turpitude include rape and sexual abuse. Non-citizens have also been deported from the U.S. for failing the register as a sex offender.
Can a sex offender’s record be sealed in Nevada? This is a tricky question and depends on a multitude of factors. Therefore, it is best to speak with an experienced attorney to better understand the specifics of the case to which you are referring.
Having said that, there are circumstances under which sexual offenses are generally ineligible for record clearing in Nevada. Those include:
Having shared all that, a sex offender can petition to remove his/her name from the Nevada sex offender registry under two circumstances:
Tier II offenders in Nevada are not eligible for early termination of their name from the list and must remain on the offender registry list for at least 25 years.
1NRS 179D.441
2NRS 179D.443
3NRS 179D.447
4NRS 179D.460
5NRS 193.130
6NRS 200.030
7NRS 200.366
8NRS 200.368
9NRS 200.400
10NRS 200.405
11NRS 200.408
12NRS 200.508
13NRS 200.710 – NRS 200.730
14NRS 201.180
15NRS 201.210
16NRS 201.220
17NRS 201.230
18NRS 201.450
19NRS 201.560